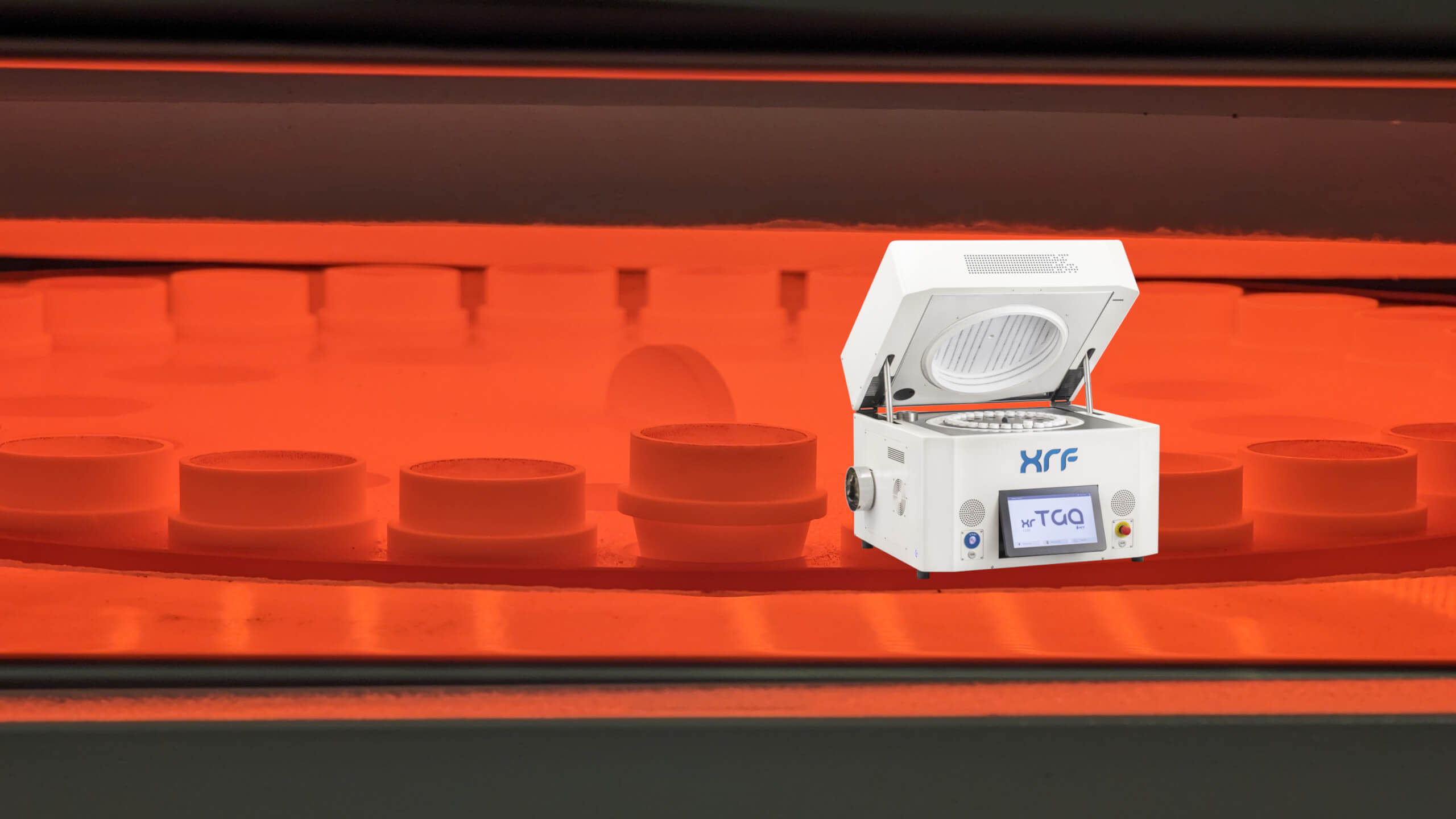
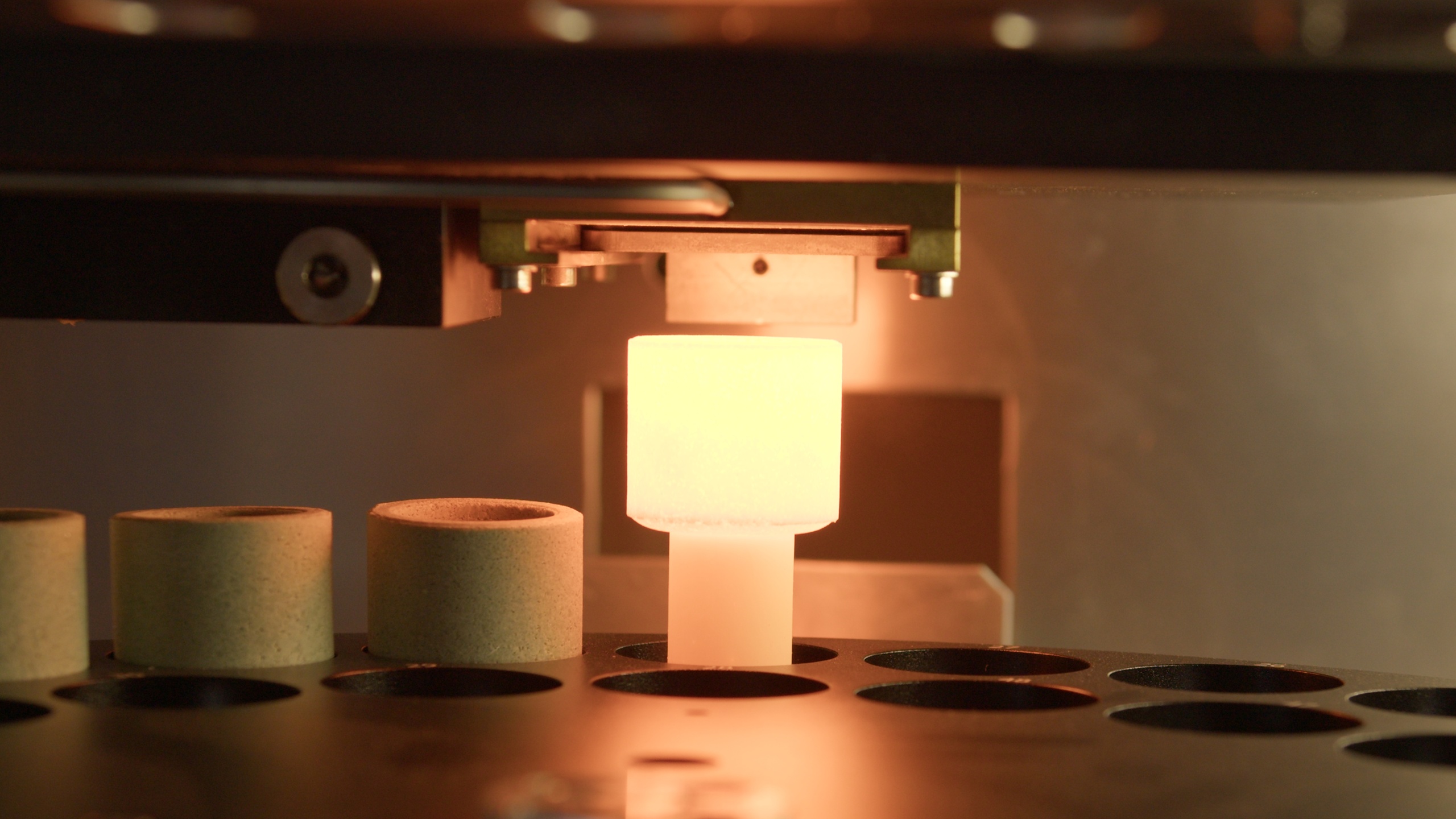
Latest News
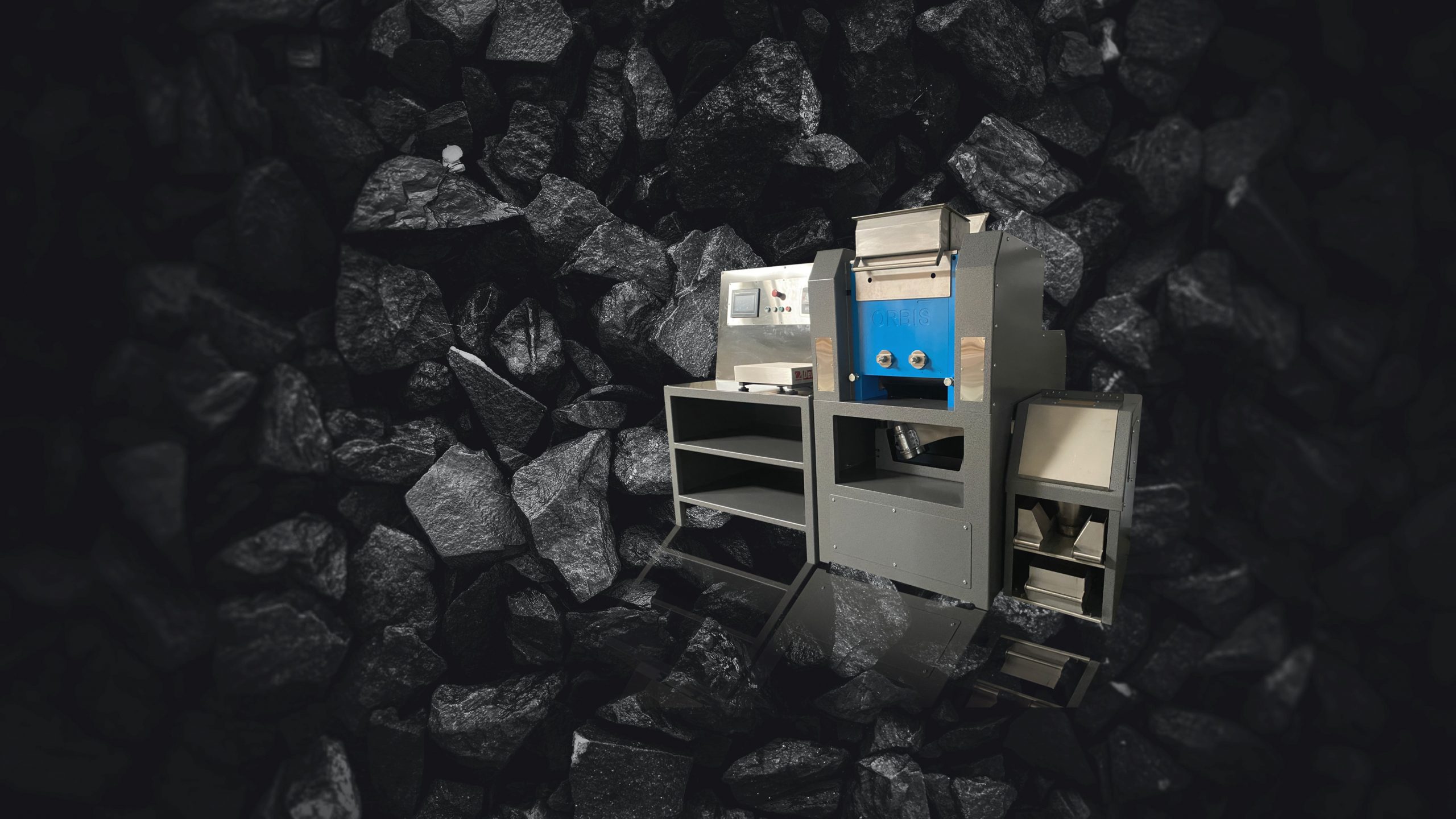
Pressed Pellets vs. Fusion Beads: Which Method Wins for Lower-Grade Deposit Optimization?
The transition to renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics has intensified global reliance on lithium, copper, and rare earth elements (REEs). At the same time, declining head grades, complex mineralogy, variable gangue chemistry, and tighter capital discipline are compressing operating margins and increasing processing costs per tonne in new mine developments and expansion projects. Many new feasibility-stage and newly commissioned mining operations advancing lower-grade lithium, copper, and rare earth deposits now proceed at head grades of these target elements close to economic cut-off, where minor fluctuations in reported elemental concentrations can shift resource classification or recovery forecasts. High-quality elemental data generated by X-ray fluorescence
...
Why XRF is Critical for Lithium Miners (Even if it Doesn’t Measure the Li)
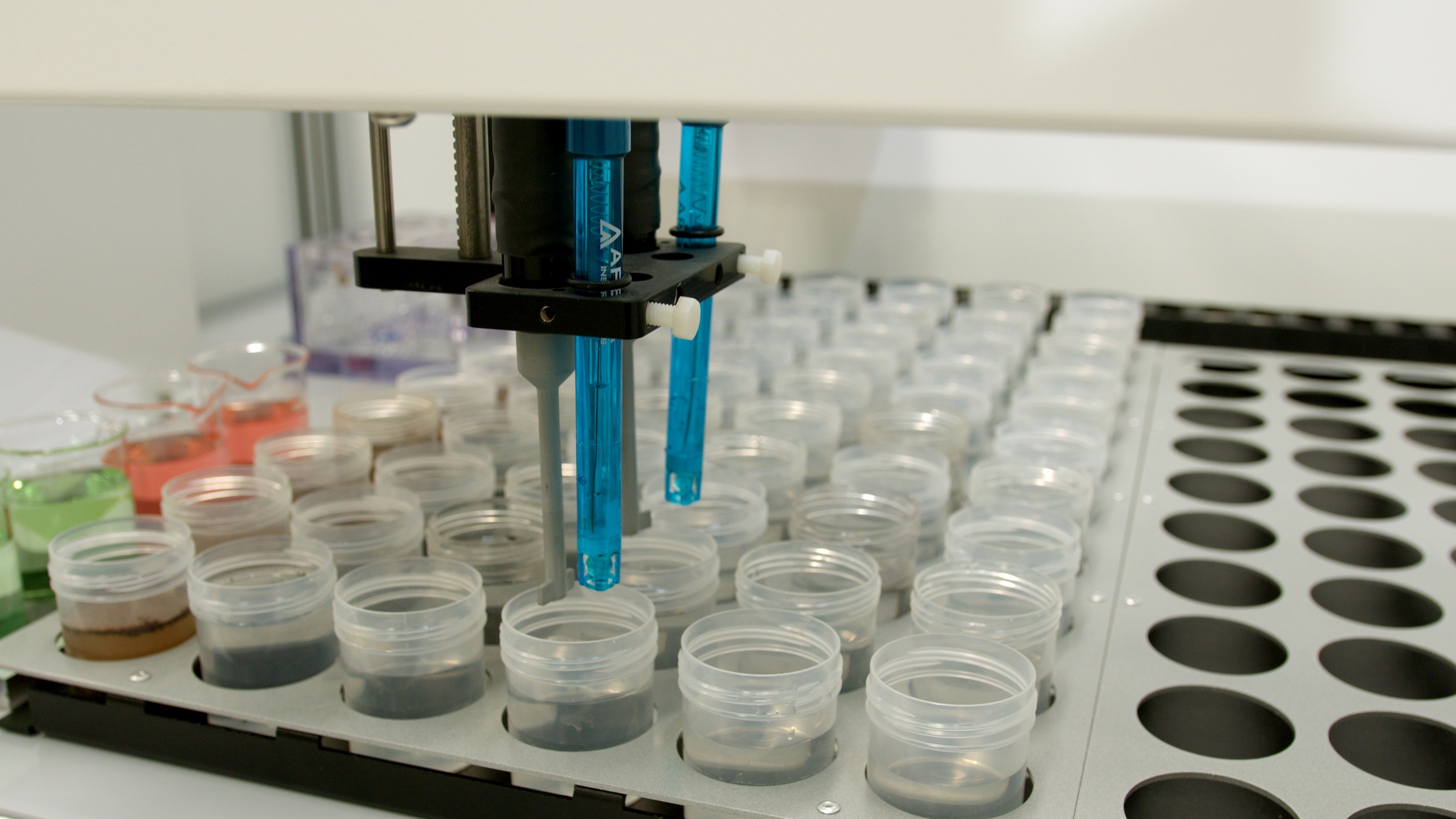
Lithium mining has shifted from discovery to optimization. As operators process lower-grade, more complex deposits, operating margins and processing efficiency depend on precise chemical control across the flowsheet. At first glance, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) may appear ill-suited because it cannot directly measure lithium in fused samples. Yet recovery is rarely limited by lithium concentration alone. It is governed by the surrounding element matrix, including iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, sulfur, and trace elements that influence roasting, leaching, and impurity control. XRF measures the chemistry that ultimately controls reaction stability, impurity behavior, and yield. Even without directly measuring lithium, it provides the elemental visibility required to protect recovery an
...
Optimizing Rare Earth Element (REE) Recovery with XRF Sample Fusion Prep
Rare Earth Elements (REEs) are seldom distributed evenly within an ore body. They occur in discrete, often refractory mineral phases where crystal structure and particle size directly influence analytical response. Conventional pressed powder pellets prepared from finely ground ore samples can struggle to represent this heterogeneity, introducing mineralogical and particle-size bias into X-ray fluorescence (XRF) data used for grade control and metallurgical planning. Across the rare earth value chain, incremental recovery gains depend on removing this analytical uncertainty. Fusion-based XRF sample preparation dissolves the mineral lattice into a homogeneous glass bead, delivering precision and comparability that enable tighter process control, improved recovery forecasting, and more ac
...